Robert Prechter Discovers Rational Expectations
Robert Prechter’s latest Global Market Perspective argues that:
movements in the cash target rate set by Australia’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA), appear to follow those in 3-month Australian Treasury Bills. After decisive moves up in T-bills from 2006 to early 2008, for example, the RBA faithfully raised its target. T-bills have since led the RBA during the financial crisis of the past year. In fact, the record indicates that the RBA almost always follows T-bills over time.
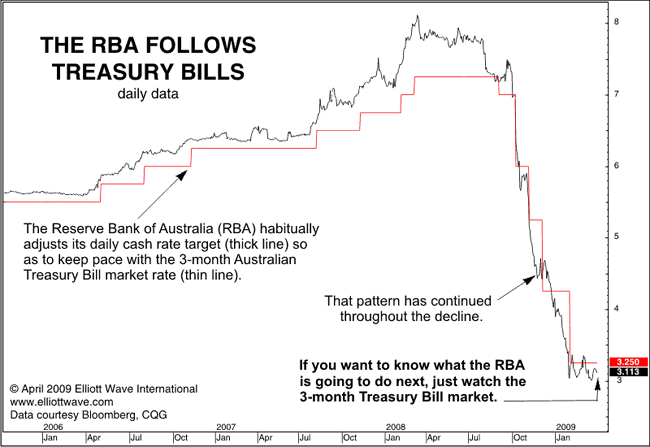
The proper conclusion to draw… is that their interest-rate decisions are not proactive, but reactive, and that they continually follow in the footsteps of the market for lack of any other useful guide…. The myth of central bank potency is so pervasive that conventional analysts can’t even imagine a better explanation for price trends: that the market is the dog wagging its central bank tail, not the other way around.
The fact that market-determined interest rates lead official interest rates does indeed have a better explanation: the market successfully anticipates central bank policy actions. This does not render central bank policy actions ineffective, as Prechter would have us believe. Indeed, it makes monetary policy more potent, because central banks can influence monetary conditions through open mouth rather than open market operations. But it does point to the fact that both market and official interest rates are largely endogenous to economic activity. Both the market and central bank look at the same data in much the same way, drawing similar conclusions. The main difference is that the markets make these judgments every day, while the central bank acts on them more slowly.
posted on 26 April 2009 by skirchner
in Economics, Financial Markets
(3) Comments | Permalink | Main
|

Comments
I think the chart is a little misleading. Virtually no one (and I don’t think the market) expected the 1% official rate cut in early October 2008, yet the chart makes it look like the official cut and the bill rate fell at the same time. The bill rate would have fallen immediately after the cut in the official rate, but the timeframe would have been too short to be noticeable on a chart like this.
Posted by .(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address) on 04/27 at 01:52 PM
From Feb 08 the cash rate target change has been announced the same day as the Board meeting, but with effect from the following day. So the bill yield reacts after the announcement, but before the actual target change. This might make the bill yield appear a little more forward-looking in the chart.
Posted by skirchner on 04/27 at 05:50 PM
For Prechter everything is endogenous, set by the social mood trends.
Posted by .(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address) on 04/28 at 09:49 PM